初级SQL
1. 什么是SQL?
结构化查询语言(Structured Query Language,SQL):用于管理和操作关系数据库的标准语言
- 数据定义语言(Data-Definition Language,DDL):定义和管理数据库结构
- 数据操纵语言(Data-Manipulation Language,DML):查询和操作数据库中数据
- 数据控制语言(Data-Control Language,DCL):控制对数据库对象的访问权限等
- 事务控制语言(Transaction-Control Language,TCL):管理数据库事务
以下都是基于书本中的大学数据库模式,可以参考这个链接下载
2. DDL
2.1 DDL定义什么?
模式(Scheme):是以下数据库对象的集合体
- 关系/表(Table):表的结构,即表名、属性名
- 域(Domain):每个属性可以存储的数据类型和范围
- 约束(Constraints):用于确保数据的有效性和一致性
- 视图(Views):用于简化复杂查询并增强安全性
- 索引(Indexes):用于提高查询性能
- 权限(Privilege):控制用户对数据库对象的访问权限
- 存储过程(Stored Procedures):描述数据在物理存储上的组织方式
- 函数(Functions):可重用的代码块,用于执行特定的操作并返回一个值
DDL涉及的SQL命令:CREATE, DROP, DELETE, ALTER, RENAME
2.2 基本数据类型
| 标识符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| char(n) | 指定长度n的固定长字符串 |
| varchar(n) | 指定最大长度n的可变长字符串 |
| int | 整数 |
| float | 单精度浮点数 |
| numeric(p,d) | 指定有p位数字,且小数点右边有d位数字 |
char类型的值会在字符串末尾自动补充空格来达到固定长度,所以即使char和varchar类型存储相同的值,比较的结果也有可能是不同的
2.3 创建关系
通用形式(A表示属性名Attribute,D表示数据类型Data)
1 | create table r( |
码约束
1 | -- 主码约束 |
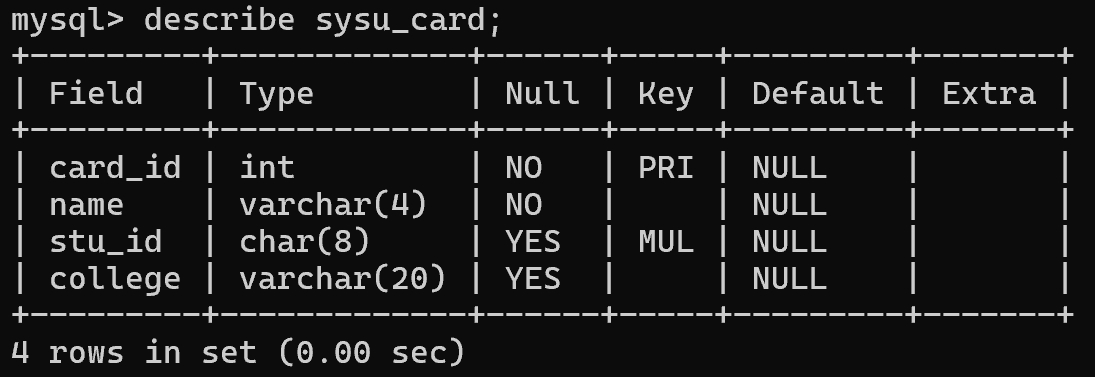
举例:创建中山大学学生卡的关系
1 | create table sysu_card( |
查看关系
1 | describe <table_name>; |
2.4 修改关系
| 操作 | 命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 删除表 | drop table r; | 不仅删除r的所有元组还删除r的模式 |
| 清空表 | delete from r; | 删除r的所有元组但保留关系 |
| 添加属性 | alter table r add A D; | r是现有关系,A是属性名,D是属性类型 |
| 去除属性 | alter table r drop A; | 注意这里只能是drop不能是delete |
3. DML
3.1 查询:SELECT
含义:为from子句中指定的关系产生笛卡尔积,然后应用where子句中指定的谓词,最后筛选输出select子句中指定的属性
- select:列出查询结果中所需要的属性
- from:列出需要访问的关系表
- where:列出作用在关系的属性上的谓词
1 | select A1,A2,...,An |
必须以select、from、where的次序写出
附加用法
- distinct关键字:在select后插入,表示去除重复属性值
- all关键字:在select后插入,表示不去除重复属性值
- 算术运算符:可以在select中对运算对象使用
+,-,*,/运算符 - 逻辑连接词:可以在where中对多个谓词逻辑使用
and,or,not连接词
单关系查询
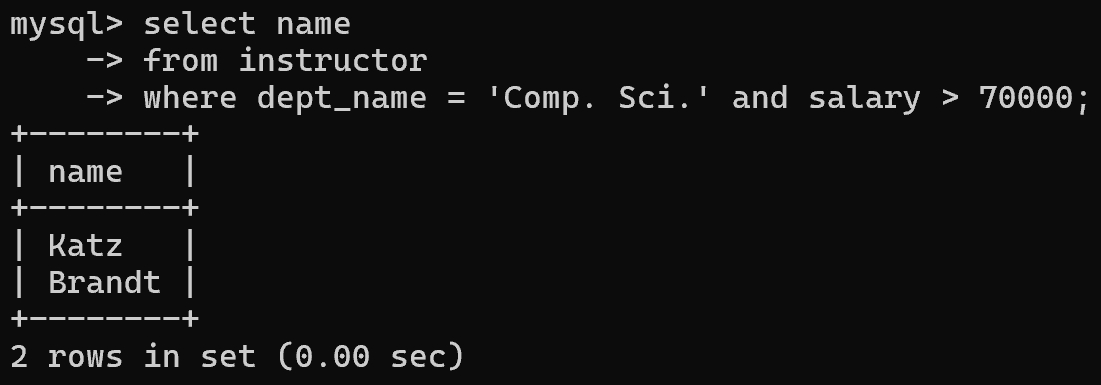
1 | -- 找出Comp. Sci.系中工资超过70000的所有老师的姓名 |
多关系查询
1 | -- 对于大学中所有讲授课程的教师,找出他们的姓名以及他们所讲授的所有课程的ID |
对于那些属于不同关系但重名的属性,必须加上关系名前缀
3.2 删除:DELETE
只能删除整个元组,无法只删除某些属性上的值
1 | -- 删除属于Finance系的教师 |
一条delete命令只能作用于一个关系
3.3 插入:INSERT
可以插入指定元组,也可以插入查询语句生成的元组集合
1 | -- 往课程中插入指定数据(要求按照定义的属性顺序排列) |
3.4 更新:UPDATE
在不改变一个元组所有值的情况下改变其某个属性的值
1 | -- 所有教师的工资将增长5% |
同步更新:相当于if-else语句,自上而下满足则赋值
1 | -- 给工资低于80000的教师涨10%,超过80000但低于100000美元的教师涨5%的工资,而给其余教师涨3% |
4. 运算符
4.1 AS
old-name as new-name
- 将长的列名或表名替换为短的别名,使查询更易读
- 在自连接或子查询中,为同一张表指定不同的别名以区分
- 为计算列、聚合函数结果或子查询结果指定一个有意义的名称
1 | -- 查询至少比Biology系某一位老师工资高的所有姓名 |
4.2 LIKE
where <属性> like <字符串模式>
- 百分号%:匹配任意字符串,如
%dasi%匹配任意包含dasi的字符串 - 下划线_:匹配任意字符,如
dasi_匹配任意前缀是dasi且长度为5的字符串
1 | -- 找出建筑名称中包含子串'Watson'的所有系名 |
在MySQL中like运算符是大小写不敏感的
4.3 *
*在select子句中表示所有属性
1 | -- 查询department表 |
4.4 ORDER BY
order by <属性> <序>:让查询结果按照某个属性的值排序显示,同时支持多列排序
- desc:降序
- asc:升序
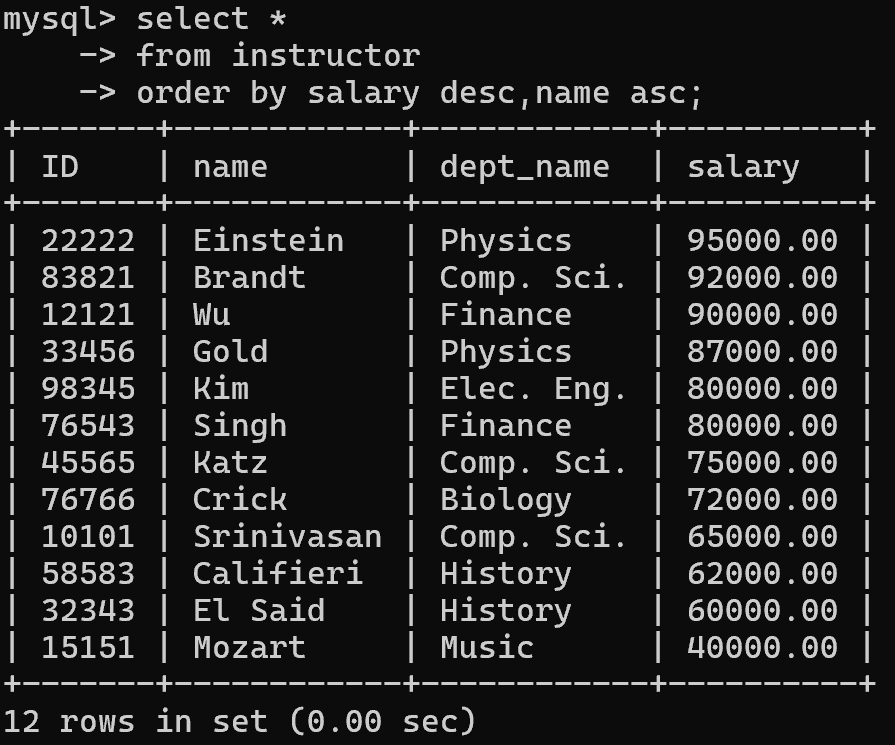
1 | -- 给出instructor关系,按照薪水降序列出,若salary相同则按name升序列出 |
4.5 BETWEEN
(not) between...and...:筛选值在或不在某个范围内的记录
1 | -- 找出薪水在90000到100000的老师的名字 |
5. 集合运算
集合运算针对查询结果,由于集合的特性,会自动去除重复,如果要保留重复项,需要显式使用关键字all
5.1 UNION
1 | -- 查询2017年秋季或2018春季开课的课程id |
5.2 INTERSECT
1 | -- 查询2017年秋季且2018春季开课的课程id |
5.3 EXCEPT
1 | -- 查询2017年秋季但2018春季不开课的课程id |
6. NULL
NULL:空值,用于表示某个字段没有有效数据
UNKNOWN:是除了FALSE和TRUE之外的第三个逻辑值
- 空值与任何值(包括空值)的比较情况都是
UNKNOWN - 空值与任何值的逻辑结果都是
UNKNOWN NOT UNKNOWN的值还是UNKNOWN- 聚合函数会忽略空值
- 唯一约束允许列中存在多个空值
WHERE子句只认可TRUE,不接受UNKNWONNULL在排序中被认为是最小的值- 只能使用
IS NULL或IS NOT NULL来判断空值
7. 聚集
7.1 聚集函数
聚集函数(aggregate):以集合为输入,返回集合中值情况的函数
- 平均值:avg
- 最大值:max
- 最小值:min
- 总数:sum
- 计数:count
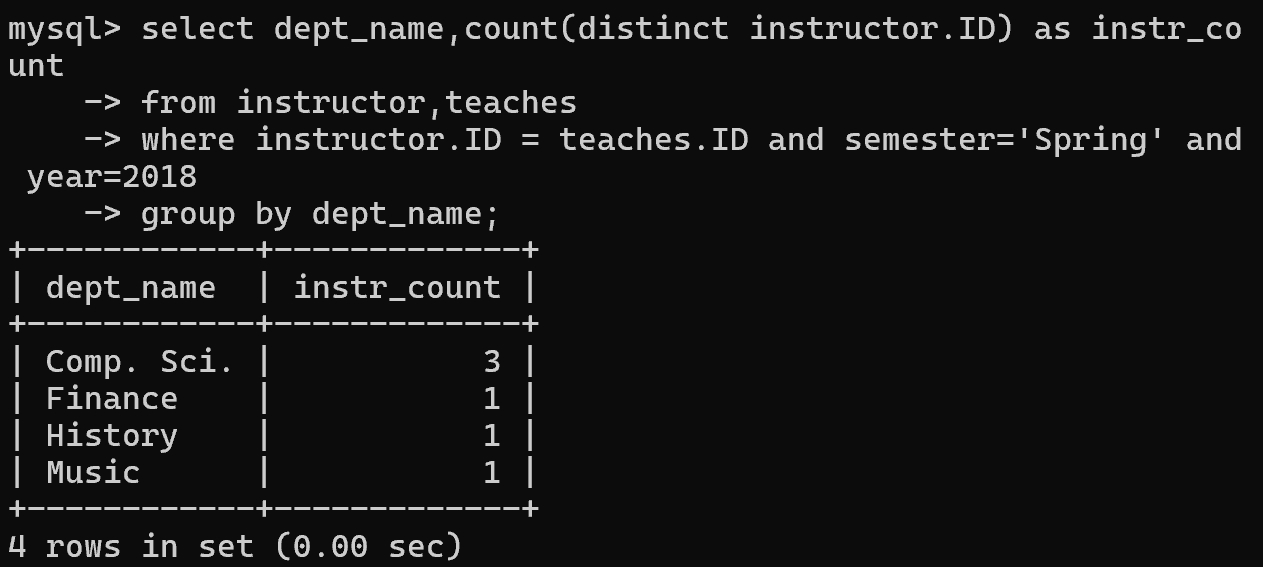
1 | -- 找出在2018年春季授课的教师总数 |
7.2 GROUP BY
group by <属性>:根据一个或多个属性的值来构造分组,从而将聚集函数作用在多个分组上
如果在select中使用聚集函数,select选择的属性,必须是group by使用的属性
1 | -- 找出每个系的平均工资 |
7.3 HAVING
having <谓词表达式>:专门用于对分组限定条件
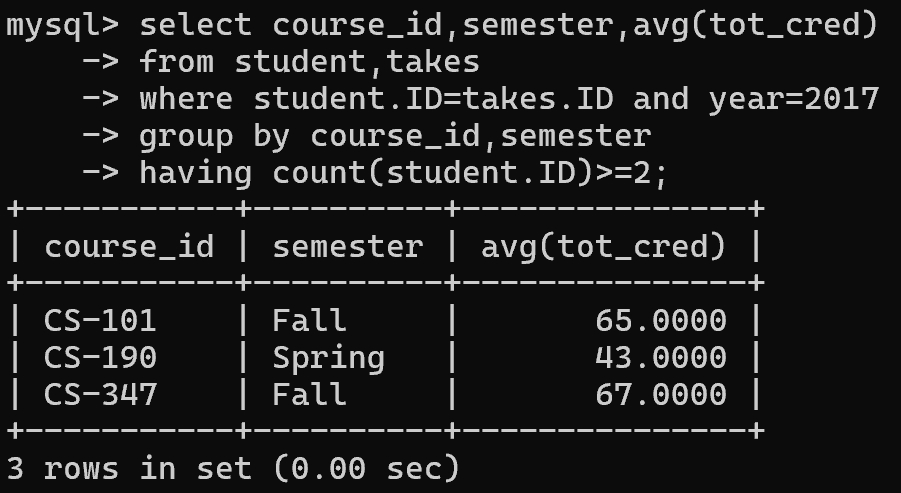
1 | -- 对于2017年中至少有2名学生选课的课程,查询每个课程的学生的总学分的平均值 |
作用顺序与含义
| 顺序 | 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | from | 选出一个关系A |
| 2 | where | 将谓词作用在关系A上,得到关系B |
| 3 | group by | 对关系B进行分组,得到若干个关系C |
| 4 | having | 将谓词作用在不同关系C上,得到关系D |
| 5 | select | 将聚集函数作用在不同关系D上 |
8. 嵌套子查询
嵌套子循环都需要加括号
相关子查询:是一个概念,指的是来自外层查询的相关名称可以用在where子句的子查询中
8.1 在where中嵌套
8.1.1 IN
(not) in (<子查询>):检查某个值是否在子查询结果中
1 | -- 查找在2017秋季开课但2018春季不开课的课程ID |
8.1.2 SOME 和 ALL
some (<子查询>):检查某个值是否满足与子查询结果中的任意一个值的比较条件
1 | -- 找出工资至少比'Biology'系某位教师的工资要高的所有教师的姓名 |
all (<子查询>):检查某个值是否满足与子查询结果中的所有值的比较条件
1 | -- 找出那些工资大于所有系平均工资的系名 |
=some等价于in,但是<>some不等价于not in<>all等价于not in,但是=all不等价于in
8.1.3 EXISTS
(not) exists (<子查询>):检查子查询返回的结果是否为空
1 | -- 找出在2017年秋季学期和2018年春季学期都开课的所有课程 |
8.1.4 UNIQUE
(not) unique (<子查询>):检查子查询返回的结果是否具有唯一性
1 | -- 找出在2017年最少开设两次的所有课程 |
8.2 在from中嵌套
子查询的结果作为父查询的目标关系,需要使用as运算符对子查询结果的属性重新命名
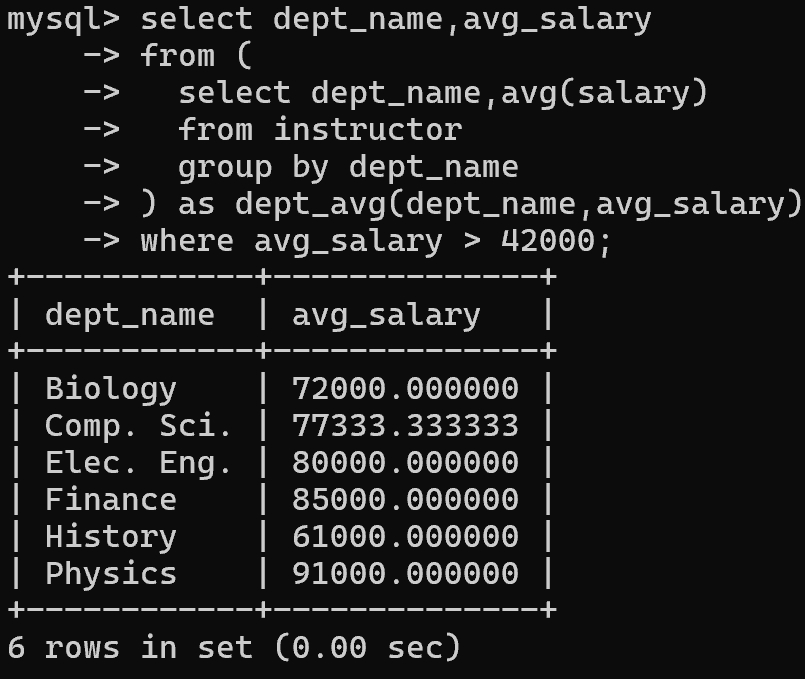
1 | -- 找出系平均工资超过42000美元的那些系的教师平均工资 |
8.3 with
with <临时关系> as (<子查询>):定义临时结果集,以便在后续查询中重复使用
1 | -- 找出工资总额大于所有系平均工资总额的所有系 |
8.4 标量子查询
就是利用聚合函数只返回单个值的子查询,适用于计算、比较或作为表达式的一部分
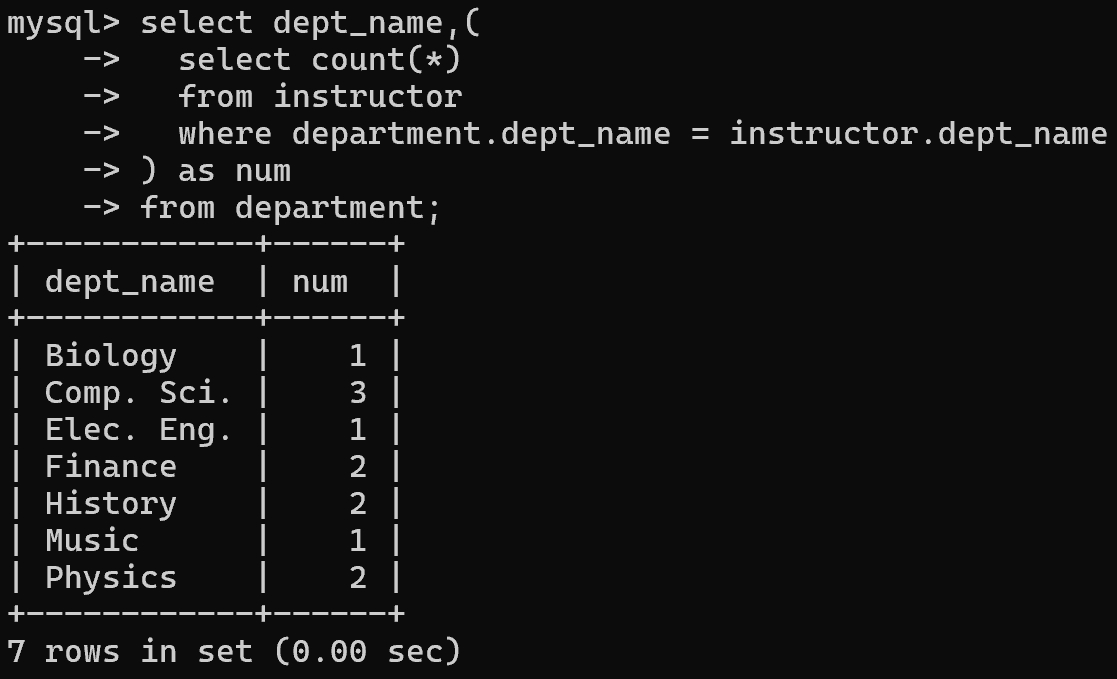
1 | -- 列出所有的系以及每个系中的教师总数 |